Cemented Acetabular Cup System

The Cemented Acetabular Cup System was designed specifically for patients who either require immediate mobilization following the surgery or are not suitable for uncemented acetabular cup options. As a result of immediate cup stability in the cement mantle, a fast postoperative patient mobilization is possible. This ensures a shortened patient hospitalization and recovery time1.
The Cemented Acetabular Cup System consists of five different models: Lubinus Cup, IP Cup, FAL Cup, FC Cup and the Endo-Model Cup. All Cemented Acetabular Cups are made of standard polyethylene (UHMWPE). In addition to the standard UHMWPE version, the IP Cup, Lubinus Cup and FAL Cup are available as cross-linked UHMWPE (X-Linked) versions. The Cemented Acetabular Cups are available in a size range starting from 38 mm up to 71 mm depending on the model, and are suitable for use with ceramic as well as CoCrMo heads. The outer design is defined by vertical and horizontal grooves for cement fixation. These surface grooves create a high degree of cement contact and allow air to escape when the implant is pressed into the cement bed4. Furthermore, spacers on the rear surface of the acetabular cup permit a uniform cement coating. This surface design increases cup stability in the acetabulum, thereby largely eliminating the risk of loosening. This cup design is used successfully in the FAL, IP Cups and Lubinus Cup.
Lubinus Cup
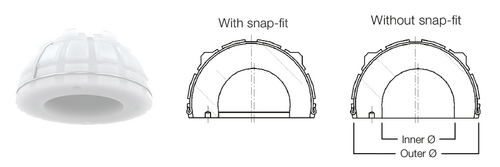
The exceptional feature of Lubinus Cup is the high cup rim, which projects beyond the spherical shape. This cup geometry reduces any luxation risk, which is further decreased by an additional snap-fit version. Another feature of the acetabular cup is its eccentric shape. This facilitates maximum material thickness in the main load-bearing zones (cranial)4.
In combination with SPII Model Lubinus Hip Stem, Lubinus Cup offers an outstanding, anatomically adapted cemented hip implant. Lubinus Cup is available in both standard UHMWPE and highly cross-linked polyethylene X-Linked.
IP Cup
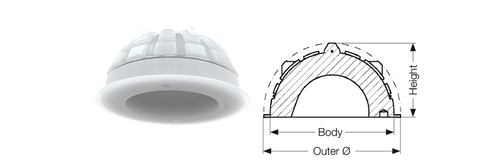
The IP Cup as well as Lubinus Cup is designed with a high cup rim, which projects beyond the spherical shape. The IP Cup differs from the Lubinus Cup in integrated chamfer at the cup entrance. This gives the patient a wider range of motion due to the design where the neck of the prosthesis strikes the cup rim later.
The IP Cup is a cemented acetabular cup made of UHMWPE: both versions of IP Cup from standard UHMWPE and X-Linked UHMWPE are possible.

FAL Cup
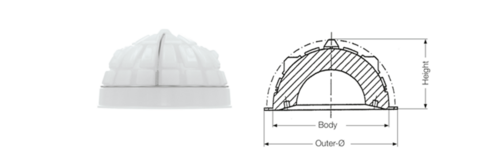
Same as other cemented acetabular cups, the design of FAL Cup with vertical and horizontal grooves in the surface creates a high degree of cement contact and allows air to escape when the implant is pressed into the cement bed4 with a uniformed cement mantle. In addition, the FAL Cup has a peripheral rim, unlike the IP Cup or the Lubinus Cup. This rim increases the cement compression, which increases cup stability in the cement matle7.
FC Cup
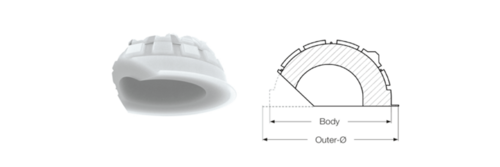
FC Cup has integrated high cup rim, which projects beyond the spherical shape. The FC Cup differs from the FAL Cup in integrated chamfer at the cup entrance. This gives the patient wider range of motion due to increased distance to a contact point between the cup rim and the implant neck. In addition, unlike the IP Cup and the Lubinus Cup, the FC Cup has a peripheral rim.
Endo-Model Cup
The Endo-Model Cup features an integral medioventral recess, which provides a wide range of motion and protects the femoral nerve together with psoas tendon. Psoas tendon or femoral nerve can be irritated by the cup rim in case of larger cup diameters.4 In addition, Endo-Model cup has a partial peripheral rim, unlike the IP Cup and the Lubinus Cup. This rim increases the cement compression resulting in a better cup stabilization in the cement mantle.7
Due to its anatomically adapted medio-ventral cut-out, Endo-Model Cup comes in two versions: right and left. Both versions have a circulating flange around the cup, except for the cut-out.
UHMWPE and X-Linked polyethylene
LINK has decades of experience in the use of UHMWPE and this was particularly valuable in the design of the cemented acetabular cups. The high quality of the polyethylene demonstrably minimizes abrasion suffered by the components, thereby reduces the risk of osteolysis. Consequently, the incidence of component loosening is very low. In addition to the Standard UHMWPE, we also supply the system in acetabular cups made of X-Linked UHMWPE. This highly crosslinked polyethylene makes it possible to achieve even lower abrasion levels.2, 3
In addition to the material properties, the external shape of the acetabular cups help to prevent loosening. Vertical and horizontal grooves in the surface create a high degree of cement contact and allow air to escape when the implant is pressed into the cement bed.4 Approximately 0.5 mm of play between prosthesis head and acetabular cup allows for “lubrication” by body fluids6. Furthermore, spacers on the rear surface of the acetabular cup permit a uniform cement coating. This surface design increases the stability of the cup in the acetabulum, thereby largely eliminating the risk of loosening.5 This design is used successfully in the FC, FAL, and IP as well as Lubinus Cup.
- L. Claes, P. Kirschner, C. Perka und M. Rudert, AE-Manual der Endoprothetik - Hüfte und Hüftrevision, Heidelberg Dordrecht London New York: Springer, 2012.
- S. M. Kurtz, „Advances in the processing, sterilization, and crosslinking of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene for total joint arthroplasty“, Biomaterials 1999; 20:1659-1687.
- E. M. Brach del Prever, „UHMWPE for arthroplasty: past or future?“, J Orthopaed Traumatol 2009;10:1-8.
- H. W. Buchholz (1969), “Das künstliche Hüftgelenk”, Sonderdruck aus Materia Medica Nordmark, Nov. 1969, 21/11: 613-622
- Garellick, Kärrholm, Rogmark, Rolfson, Herberts, ANNUAL REPORT 2014; The Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register.; p. 75
- H.W. Buchholz und E. Strichte (engineering BASF), 1972
- W. Buchholz, Das künstliche Hüftgelenk, Modell St. Georg, in Der totale Hüftgelenkersatz, Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart, 1985








